-
Type 1 Error and Type 2 ErrorStats/Inferential 2020. 1. 30. 14:22
1. Overview
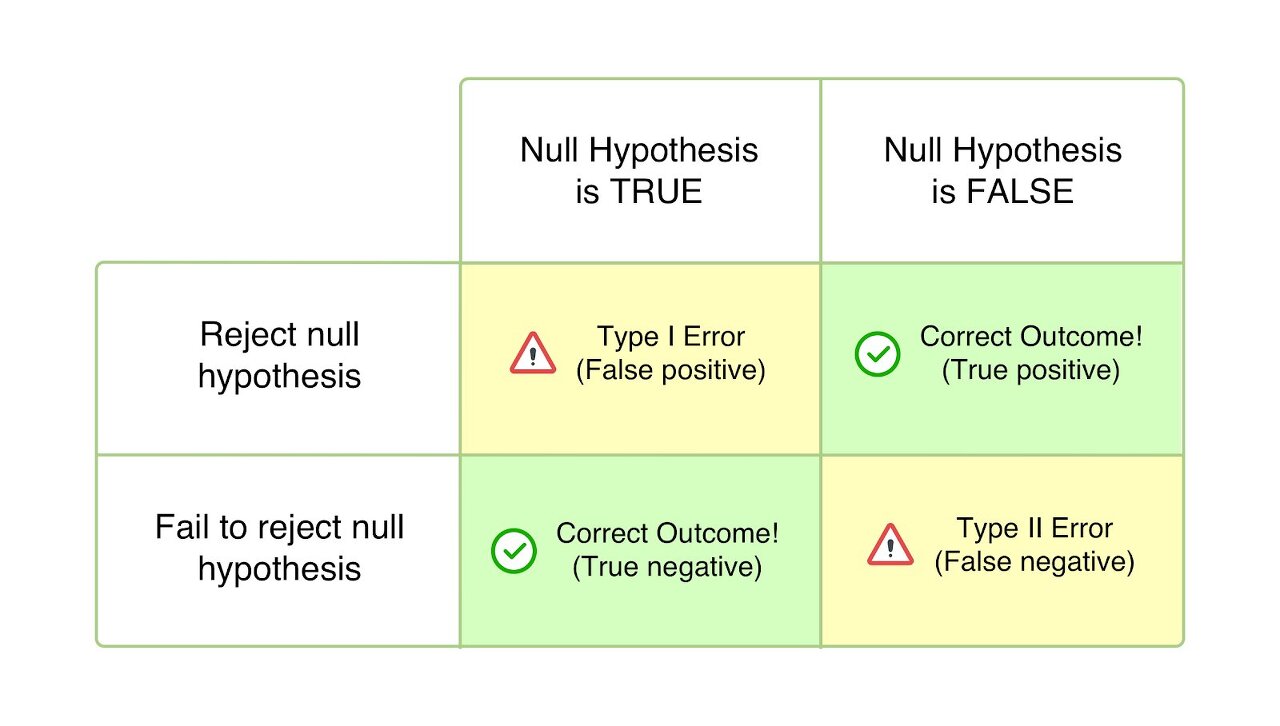
In statistical hypothesis testing, a type I error is the rejection of a true null hypothesis (also known as a "false positive" finding or conclusion), while a type II error is the non-rejection of a false null hypothesis (also known as a "false negative" finding or conclusion).
2. Description
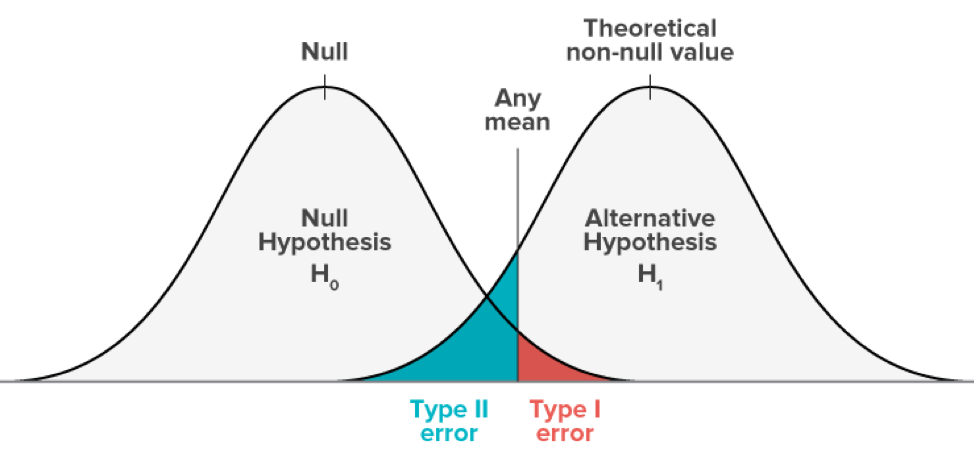
2.1 Type 1 Error $\alpha$
It is often assimilated with false positives or Level of significance – which happen in hypothesis testing when the null hypothesis is true but rejected. The null hypothesis is a general statement or default position that there is no relationship between two measured phenomena.
Simply put, type 1 errors are “false positives” – they happen when the tester validates a statistically significant difference even though there isn’t one.
2.2 Type 2 Error $\beta$
If type 1 errors are commonly referred to as “false positives”, type 2 errors are referred to as “false negatives”.
Type 2 errors happen when you inaccurately assume that no winner has been declared between a control version and a variation although there actually is a winner.
In more statistically accurate terms, type 2 errors happen when the null hypothesis is false and you subsequently fail to reject it but accepted it.
3. Reference
'Stats > Inferential' 카테고리의 다른 글
Power and Effective size (0) 2020.02.05 Lack-of-fit sum of squares and Pure-error sum of squares (0) 2020.02.04 Confidence Interval (0) 2020.01.16