-
Eventual consistency and strict consistencyModeling/TheoremParadigm 2019. 9. 28. 21:23
1. Overview
Let’s define eventual consistency vs strict consistency.
2. Description
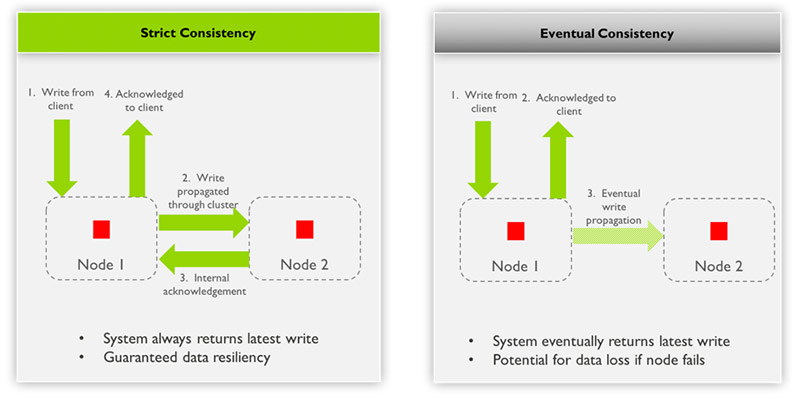
2.1 Strict consistency(or immediate or strong)
- For any incoming write operation, once a write is acknowledged to the client, the updated value is visible on reading from any replicated node (server) in the system
- Guaranteed data resiliency
- Once a write is acknowledged to the client the update is protected from node failure with redundancy
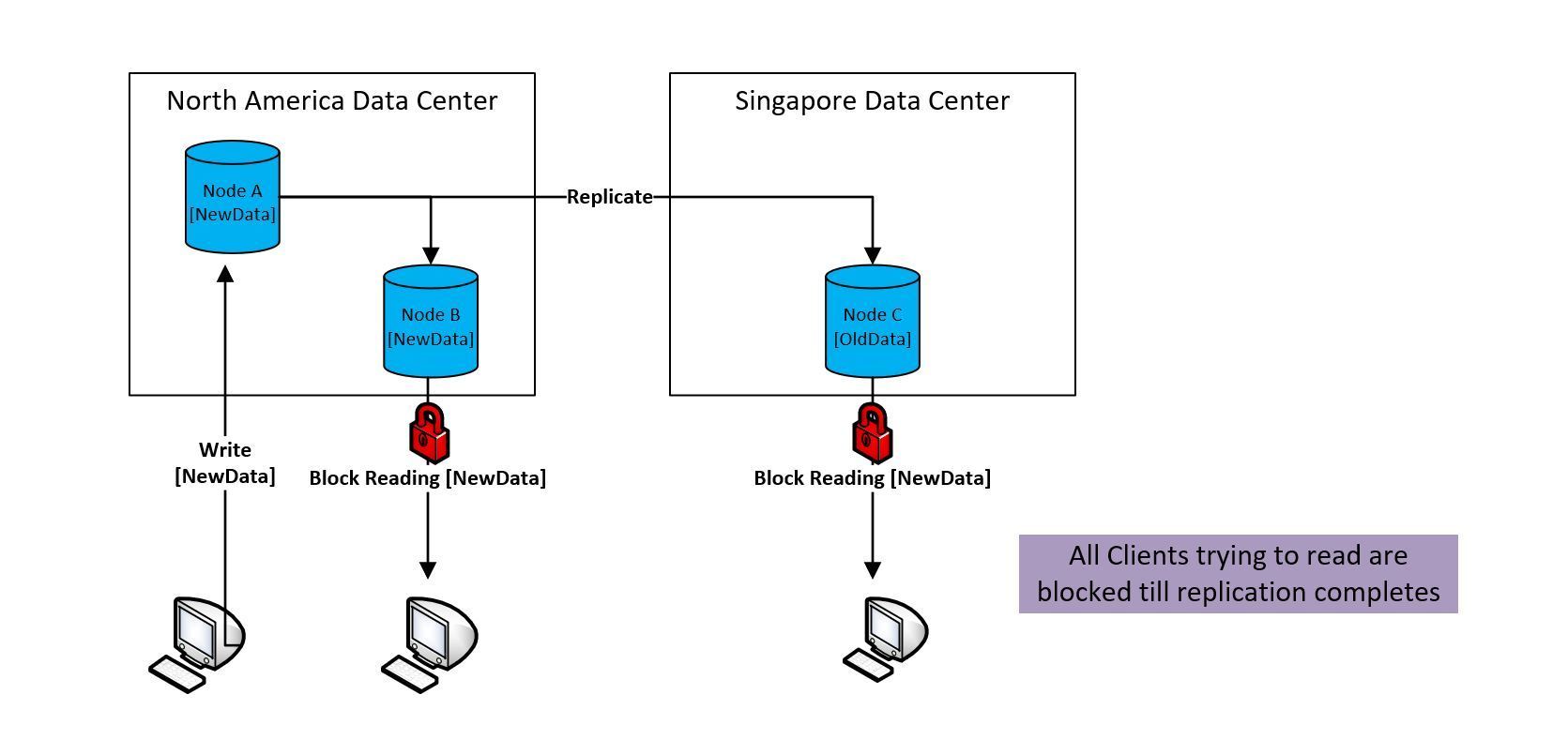
- This effectively means that all readers are blocked until replication of the new data to all the nodes is complete
2.1.1 Where strict consistency is needed
- Scale-out file storage
- Scenario: The data is written to only one node (on NVRAM) and acknowledged. An enterprise customer once explained to me that under heavy load, a node may get marked offline. Effectively it’s down, resulting in clients getting “File-Not-Found” errors for files they had successfully written just a few seconds prior. This wreaks havoc on their applications.
- Instant recovery from backup
- If a failure happens on the recovery node, the application fails and the system loses live production VM data
- Data Recovery and Protection
2.1.2 Limits of strict consistency
- Being able to have a detrimental effect on system and performance, depending on the scenario
2.2 Eventual consistency
- All nodes are always available to be read but some nodes may have stale data at a particular point of time
- Potential for data loss if the node fails

2.2.1 Usages
Some scenarios may not require strict consistency
- Photo sharing system like Flicker
- Message timeline for a social app like Facebook or Twitter
- Domain Name System(DNS)
- Adding items to a shopping cart
2.2.2 Support for Eventual Consistency in Modern Databases

3. Reference
https://www.cohesity.com/blog/strict-vs-eventual-consistency/
'Modeling > TheoremParadigm' 카테고리의 다른 글
Locking Strategies and Deadlocks (0) 2020.02.27 Database Scaling (0) 2020.02.23 Cooperative vs Preemptive Multitasking (0) 2019.11.10 Difference between Concurrency and Parallelism (0) 2019.08.18 Polymorphism, Upcasting, And Downcasting (0) 2019.08.18