-
Comparison between REST and SOAP with HTTPWeb 2019. 8. 23. 11:57
1. Overview
Let's analyze SOAP and Rest with protocols.
2. Comparison between SOAP and REST
SOAP REST History SOAP(Simple Object Access Protocol) was created in 1998 by Dave Winer, Don Box, Bob Atkinson and Mohsen AIGhosein in collaboration with Microsoft REST(Representational State Transfer) was Created in 2000 by Roy Thomas Fielding. Developed in an academic environment, this protocol embraces the philosophy of the open Web Concept SOAP makes data available as services, E.g: getUserInfoamtion, getPayments, getBook, setCostomer REST makes data available as resources, E.g: user, payments Services Back-end Services Front-end Services Media Type SOAP, WS-* JSON, XML, form-UML-encoded, custom Transports HTTP, TCP, UDP, Queues, Web Sockets, custom HTTP only Message Patterns Request-reply, one-way, duplex Request-reply only Cache SOAP-based reads cannot be cached REST-based reads can be cached. Performs and scales better Pros - SOAP follows a formal enterprise approach
- Works on top of any communication protocol, even asynchronously
- Information about objects is communicated to clients
- Security and authorization are part of the protocol
- Can be fully described using Web Service Definition Language (WSDL)
- REST uses HTTP Verbs such as: GET, POST, PUT, DELETE
- Relatively easy to implement and maintain
- Clearly separates client and server implementations
- Communication not controlled by a single entity
- Information can be stored by the client to prevent multiple calls
- Can return data in multiple formats(HTML, JSON, XML, Plain text, PDF, etc.)
- Can be consumed by any client, even a web browser with Ajax and javascript
Cons - SOAP consume a lot of bandwidth communicating metadata
- Tack much effort to implement and is not good for integrating between Web and mobile developers
- Support the Only XML
- REST works on top of the HTTP protocol
- Less authorization and security
Security Support both SSL security and WS-security, which adds some enterprise security features. Supports identity through intermediaries, not just point to point SSL. Supports only point-to-point SSL security ACID Having comprehensive support for both ACID based transaction management for short-lived transactions and compensation based transaction management for long-running transactions. It also supports two-phase commit across distributed resources. REST supports transactions, but it is neither ACID compliant nor can provide two-phase commit across distributed transactional resources as it is limited by its HTTP protocol. Used When - SOAP used when clients need to have access to objects available on servers
- When you want a formal contract between client and server
- When you need asynchronous processing and invocation
- REST used when clients and servers are both on a Web environment
- When information about objects are independent to the client
Do not use When - Do not use SOAP when you want a API that easy to use
- When your bandwidth is very limited
- Do not use REST when you need a strict contract between client and server
- When performing transactions that involve multiple calls
Commonly use for - SOAP used for Financial services
- Payment gateways
- Telecommunication services
- REST used for Social Media services
- Mobile Services
- Social Networks
Real Example - Salesforce SOAP API
- Paypal SOAP API
- Clickatell SMS SOAP API
- Twitter REST API
- LinkedIn REST API
- Slack REST API
- Processing

- Architecture

- Transmission verification Architecture
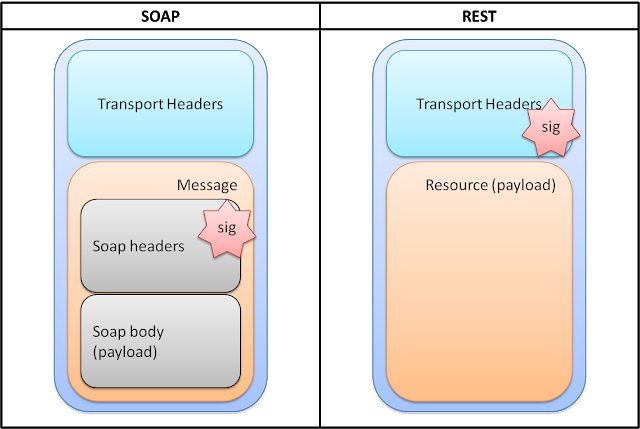
3. References
https://searchapparchitecture.techtarget.com/definition/RESTful-API
https://searchapparchitecture.techtarget.com/definition/REST-REpresentational-State-Transfer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Representational_state_transfer
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SOAP
https://liulyndon.blogspot.com/2017/08/mvc-rest-api-vs-soap-web-services.html
'Web' 카테고리의 다른 글
Web Service and Web Application (0) 2019.08.31 Cache Burst (0) 2019.08.22