-
Session and CookieWeb/Security 2019. 8. 23. 13:22
1. Overview
1.1 Session
- Storing user-related data across different requests.
- Server-side storage holding contextual data
1.2 Cookie
- Storing a small piece of the date on client-side
- Used to identify a client
- Used for passing some data from one servlet to another

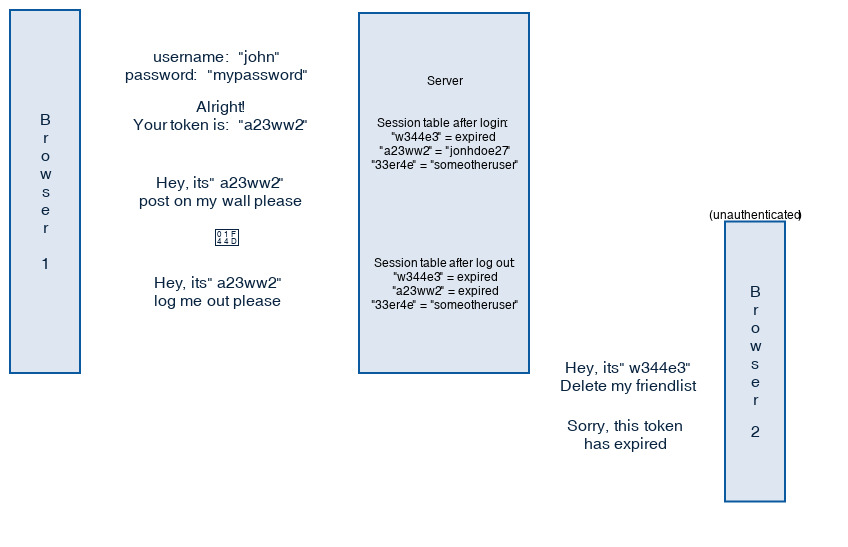
2. Session
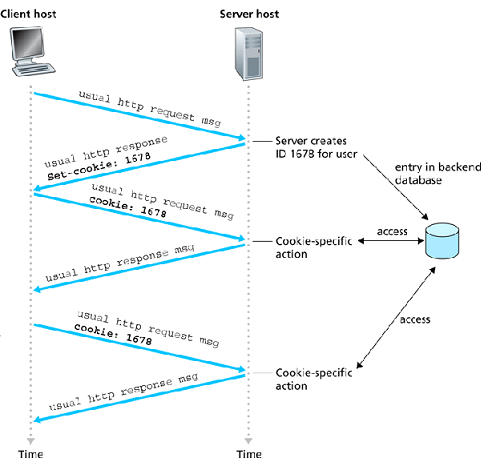
If we access the JSP page for the first time, then a new session gets created by default. In most cases, a web server uses cookies for session management. When a session object is created, then a server creates a cookie with JSESSIONID key and value which identifies a session.
2.1 Obtaining an HttpSession straightly or create a new one
HttpSession session = request.getSession();- Same with above
request.getSession(true)- Not creation, but only Obtaining existing one
request.getSession(false)- Disable default creation whenever visiting a JSP page
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" session="false" %>2.2 Session Attributes
Attributes Description setAttribute(String, Object) Creating or Replacing a session attribute with a key and a new value getAttribute(String) Reading an attribute value with a given name (key) removeAttribute(String) Removing an attribute with a given name getAttributeNames() Checking already existing session attributes invalidate() Invalidating whole data it stores which means removes the whole session from the web server so unable to access attributes from it anymore. 3. Cookie
- Defined in the javax.servlet.http package
- To send it to the client, need to create one and add it to the response
Cookie uiColorCookie = new Cookie("color", "red"); response.addCookie(uiColorCookie);3.1 Set the cookie expiration Date
uiColorCookie.setMaxAge(60*60);This set one hour validate cookie. after this time, the cookie cannot be used by a client(browser) when sending a request and it also should be removed from the browser cache.
3.2 Set the Cookie Domain
- setDomain(String)
- Allow specifying domain names to which it should be delivered by the client.
- Default is the domain name which created a cookie
3.3 Set the Cookie path
- If specifying a path explicitly, then a Cookie will be delivered to the given URL and all its subdirectories
- implicitly, being set to the URL which created a cookie and all its subdirectories
uiColorCookie.setPath("/welcomeUser");3.4 Read Cookies in the servlet
Cookies are added to the request by the client which checks its parameters and decides if it can deliver it to the current URL.
By calling getCookies() on the request HttpServletRequest passed to the Servlet
public Optional<String> readCookie(String key) { return Arrays.stream(request.getCookies()) .filter(c -> key.equals(c.getName())) .map(Cookie::getValue) .findAny(); }3.5 Remove a Cookie
To remove a cookie from a browser, have to add a new one to the response with the same name, but with a maxAge value set to 0.
Cookie userNameCookieRemove = new Cookie("userName", ""); userNameCookieRemove.setMaxAge(0); response.addCookie(userNameCookieRemove);4. References
https://www.baeldung.com/java-servlet-cookies-session
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Session_(computer_science)
https://www.sohamkamani.com/blog/2017/01/08/web-security-session-cookies/
https://anydifferencebetween.com/difference-between-cookies-and-sessions/
https://medium.com/@piraveenaparalogarajah/sessions-and-cookies-2c0919552f29
'Web > Security' 카테고리의 다른 글
Open Authorization(OAuth) 2.0 (0) 2019.08.29 Difference between Signing and Encryption with OpenPGP (0) 2019.08.29 Encoding, Encryption, Hashing, and Obfuscation (0) 2019.08.28 Authentication and Authorization (0) 2019.08.27 JWT, JWS, JWE, JWA, and JWK (0) 2019.08.27