-
Bridged, Network Address Translation (NAT), Host-only in Virtual MachineWeb/Network 2020. 3. 6. 20:48
1. Overview
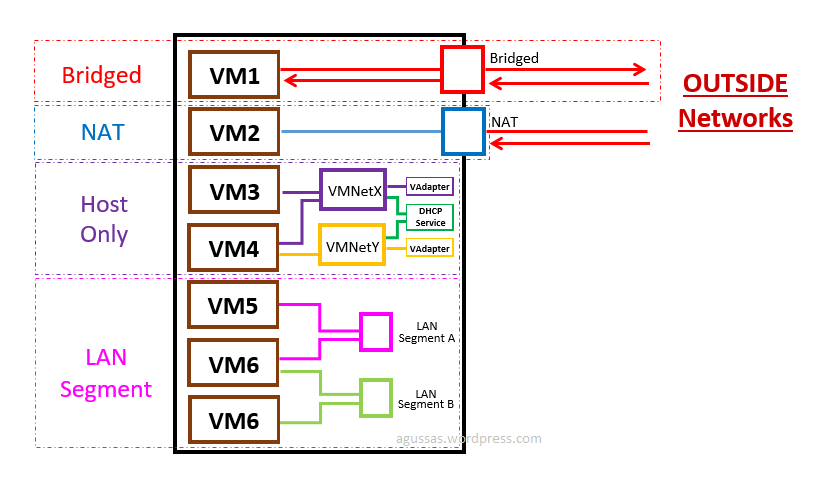
Virtual machines can communicate with each other on the host as well as other physical machines on the physical network. To do so, virtual machines need two virtual things: virtual Network Interface Card (vNICs) and virtual switches/bridges. A virtual switch is a logically defined layer-2 device that passes frames between nodes. Virtual NICs of VMs are connected to the virtual ports on the virtual switch, which is then connected through the host physical NIC to the physical network. The basic principle of network communications is the same, whether they are virtual or physical. The virtual switch is just like a physical switch. Each virtual switch creates a separate broadcast domain. To connect two broadcast domains, we need a layer-3 router.

2. Description
2.1 Host-Only
The VM will be assigned one IP, but it's only accessible by the box VM is running on. No other computers can access it.
In this mode, VMs on the host can talk with each other and with their host, but they cannot communicate with any other computers beyond. This connection mode is useful when we set up an isolated private virtual network where we can have cyber attack experiments. Within a constrained host-only environment, we can avoid leaking out packets into our normal network.
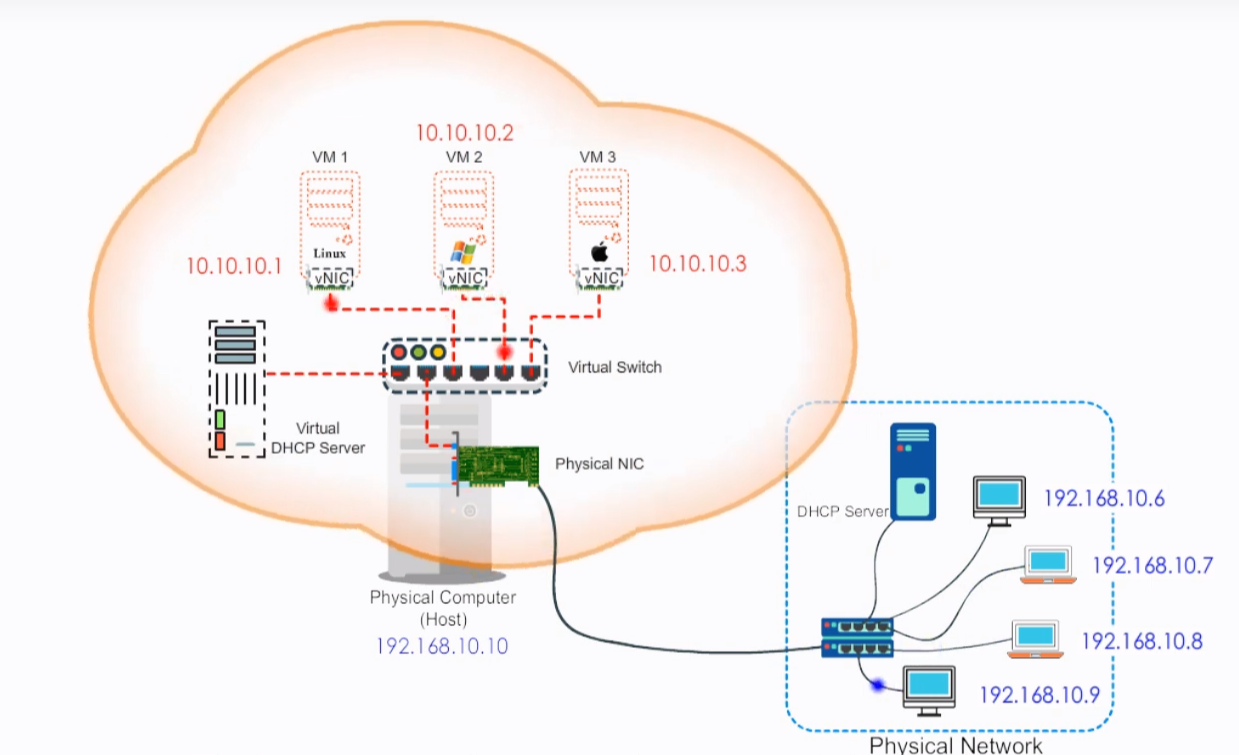
2.2 Network Address Translation (NAT)
Just like your home network with a wireless router, the VM will be assigned in a separate subnet, like 192.168.6.1 is your host computer, and VM is 192.168.6.3, then your VM can access outside network like your host, but no outside access to your VM directly, it's protected.
In this mode, VMs rely on the host to act as a NAT device. With the NAT mode, a virtual DHCP server is responsible for assigning IP addressing information to these VMs and they form a private network. Other machines on the physical network are getting IP addressing information from the physical DHCP server. They form an external network. The host is sitting between these two networks and translates the IP address from a VM to the IP address of the host. It also listens for returning traffic so that it can deliver it to the VM. The external physical network sees traffic from VMs as if it comes from the host itself. The NAT is appropriate when virtual machines are mainly used a client workstation to check emails or surf the Internet.

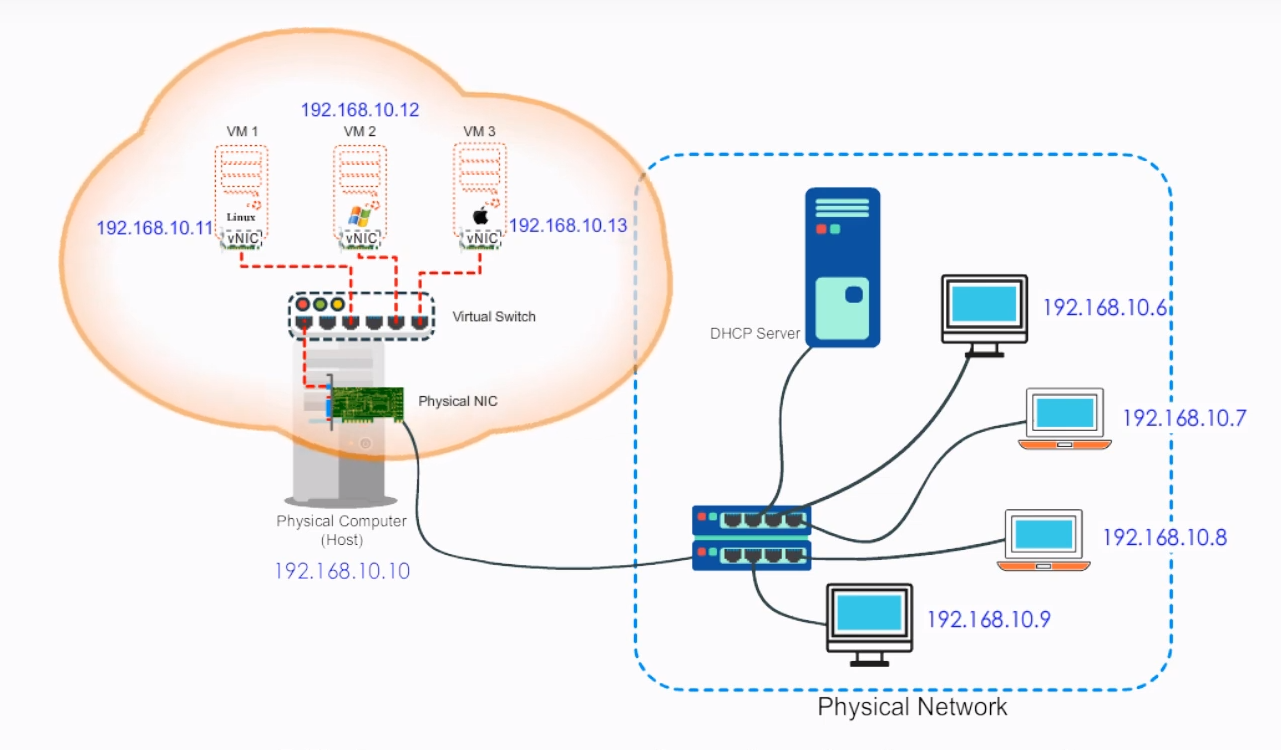
2.3 Bridged
Your VM will be in the same network as your host, if your host IP is 172.16.120.45 then your VM will be like 172.16.120.50. It can be accessed by all computers in your host network. The host's NIC is a bridge to all these VMs. Just like their host and other physical computers, VMs obtain IP address information from a DHCP server on the physical network. When connected using Bridged connection mode, a VM appears to other nodes as just another computer on the network.
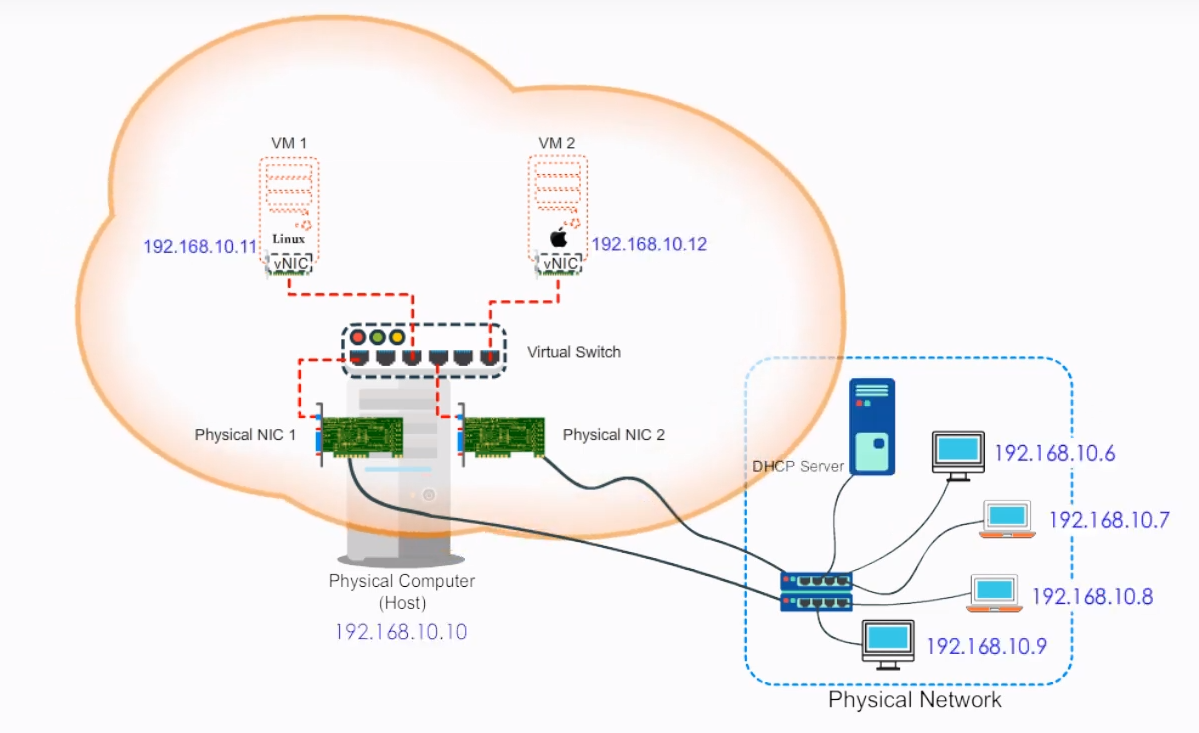
2.3.1 Dedicated physical NICs for each VM
We can install physical NICs for each VM. Each virtual NIC gets a connection to its own dedicated physical NIC. In the bridged connection mode, these VMs' IP addresses are visible and directly accessible by other computers on the network. Thus good candidates for these VMs can be a mail server, a filer server, or a web server.
3. Reference
'Web > Network' 카테고리의 다른 글
Simplex, Half duplex, and Full duplex (0) 2020.03.07 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server (0) 2020.03.06 Subnetworks and Subnetting (0) 2020.03.06 Domain Name Server (DNS), Iterative, and Recursive DNS Query (0) 2019.09.28 Difference between TCP keepalive and HTTP keepalive (0) 2019.09.28