-
Object Relation Mapping(ORM) and HibernateFramework/ORM 2020. 7. 9. 22:28
1. Overview
Object Relation Mapping(ORM) provides a simple API for storing and retrieving Java objects directly to and from the database.
2. Features

- Non-intrusive: No need to follow specific rules or design patterns
- Transparent: Your object model is unaware
3. Advantages of ORM
3.1 Productivity
Eliminates lots of repetitive code – focus on business logic – Database schema is generated automatically
3.2 Maintainability
Fewer lines of code – easier to understand – Easier to manage change in the object model
3.3 Performance:
- Lazy loading – associations are fetched when needed
- Caching
3.4 Database vendor independence
The underlying database is abstracted away – Can be configured outside the application
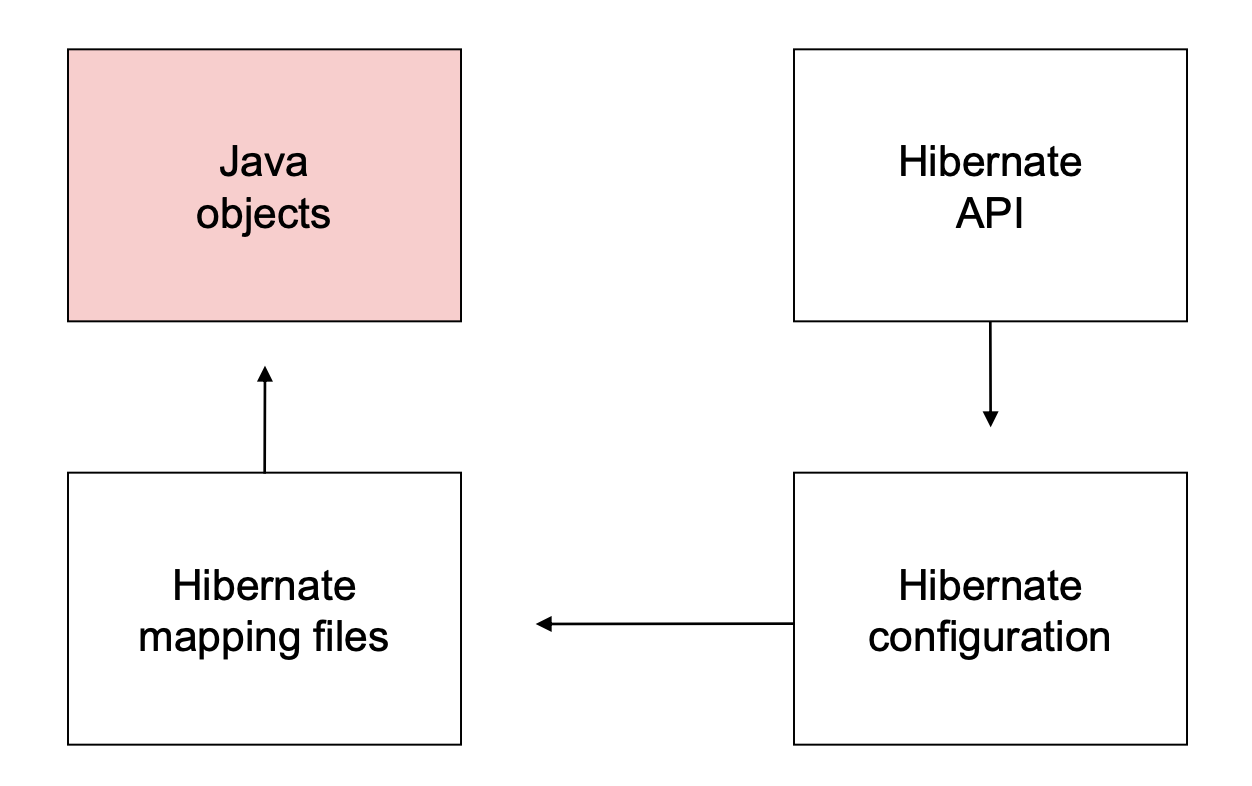
4. ORM and Architecture

5. EventManager
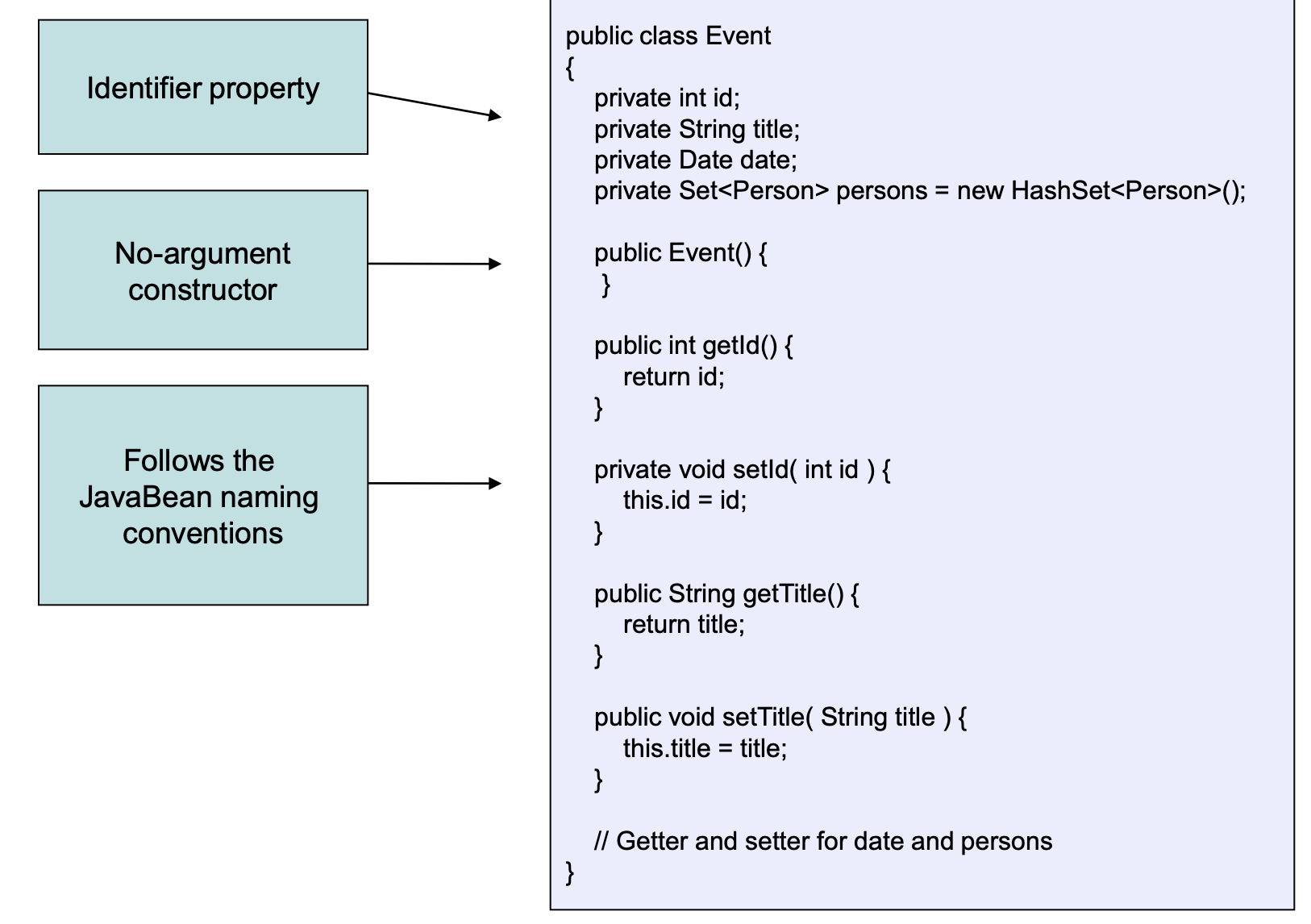
5.1 Java Objects (POJO)
5.2 Hibernate mapping files
Tells Hibernate which tables and columns to use to load and store objects
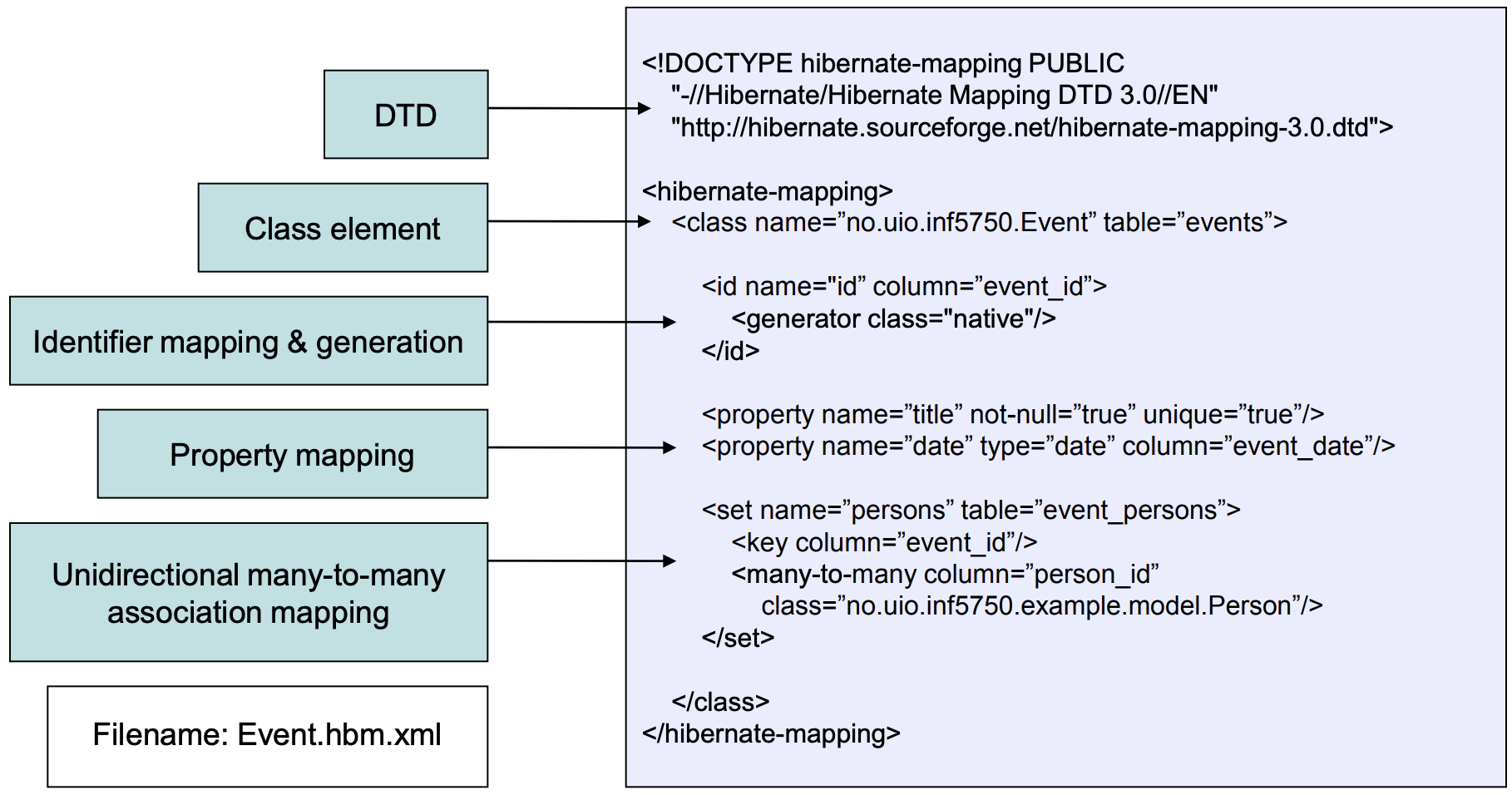
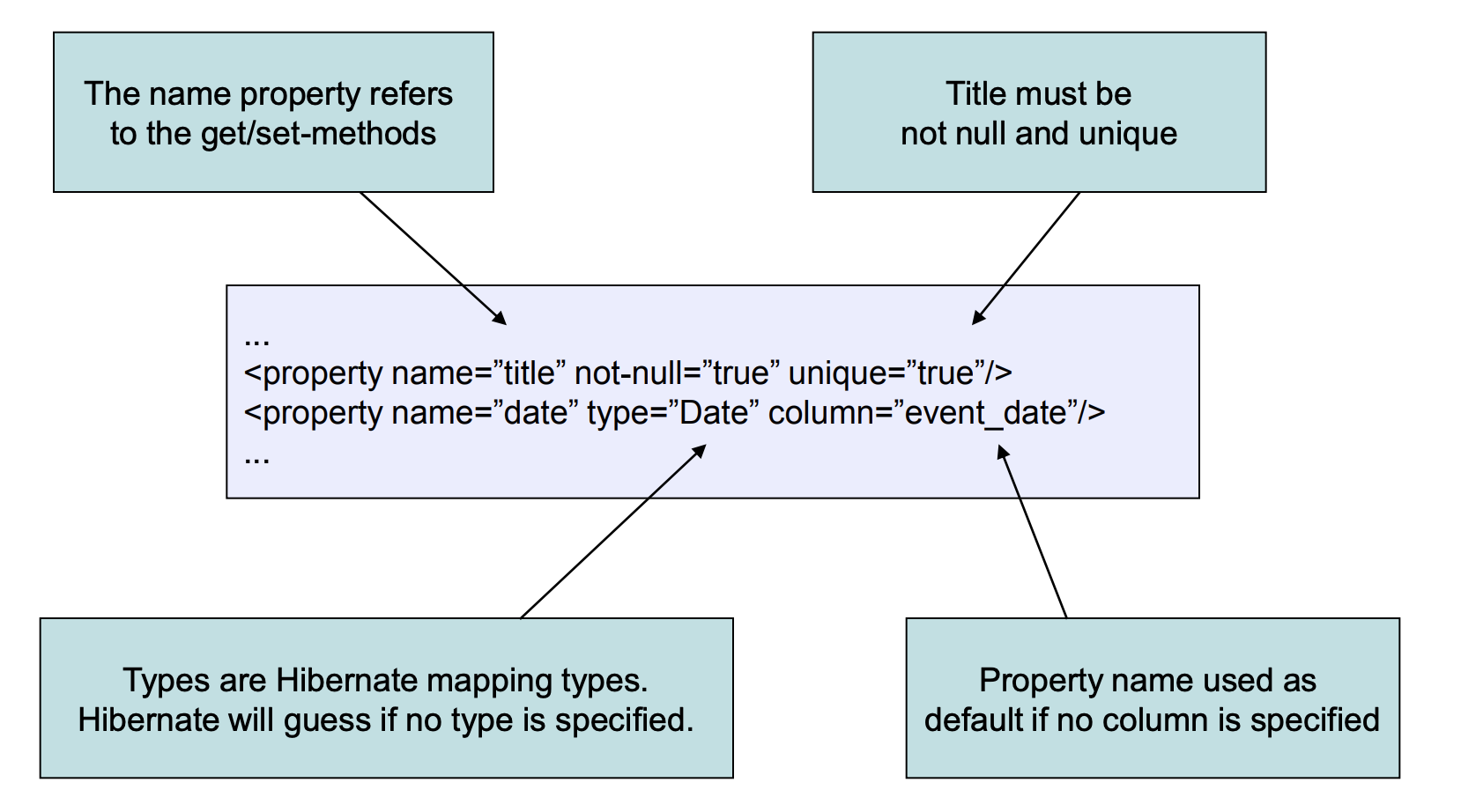
5.2.1 Property mapping
5.2.2 Association mapping

5.2.3 Hibernate mapping types
Hibernate will translate Java types to SQL / database types for the properties of your mapped classes
Java Type Hibernate Type SQL Type java.lang.String string VARCHAR java.util.Date date, time DATE, TIME java.lang.Integer, int integer INT java.lang.Class class varchar java.io.Serializable serializable BLOB, BINARY 5.3 Hibernate configuration
- Each database has a dialect – hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
- Must also specify: JDBC driver class, Connection URL, Username, Password

6. The SessionFactory interface
- Provide Session instances to the application
- Shared among application threads
- most important method is getCurrentSession
7. The Session Interface
- Obtained from a SessionFactory
- Main runtime interface between a Java application and Hibernate
- Responsible for storing and retrieving objects
- Think of it as a collection of loaded objects related to a single unit of work
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();8. Instance states
An object instance state is related to the persistence context.
The persistence context = a Hibernate Session instance
Three types of instance states:


8.1 Transient
The instance is not associated with any persistence context –
8.2 Persistent
The instance is associated with a persistence context –
8.3 Detached
The instance was associated with a persistence context which has been closed – currently not associated
9. Reference
'Framework > ORM' 카테고리의 다른 글
N+1 Problem (0) 2020.04.10