-
AWS Relational Database Service(RDS)Cloud/AWS 2020. 7. 26. 15:11
1. Overview
- It's a managed DB service for DB use SQL as a query language
- It allows you to create databases in the cloud that are managed by AWS
- Postgres
- MySQL
- MariaDB
- Oracle
- Microsoft SQL Server
- Aurora(AWS Proprietary database)
1.1 Features
- Launched within a VPC, usually in a private subnet, control network access using security groups (important when using Lambda)
- Storage by EBS (gp2 or oil), can increase volume size with auto-scaling
- Backups: automated with point-in-time recovery. Backups expire
- Snapshots: manual, can make copies of snapshots cross region
- Monitoring through CloudWatch
- RDS Events: get notified via SNS for events (operations, outages, and etc.)
- You can't SSH into your underlying DB instances
2. Advantages overusing RDS versus deploying DB on EC2
- RDS is a managed service
- Automated provisioning, OS patching
- Continuous backups and restore to specific timestamp(Point in Time Restore)
- Monitoring dashboards
- Read replicas for improved read performance
- Multi-AZ setup for DR(Disaster Recovery)
- Maintenance windows for upgrades
- Scaling capability(vertical and horizontal)
- Storage backed by EBS(gp2 or io 1)
- But you can's ssh into your instances
3. RDS Backups
- Backups are automatically enabled in RDS
- Automated backups:
- Daily full backup of the database (during the maintenance window)
- Transaction logs are backed up by RDS every 5 minutes
- Ability to restore to any point in time (from oldest back up to 5 minutes ago)
- 7 days retention (can be increased to 35 days)
3.1 DB Snapshots
- Manually triggered by the user
- Retention of backup for as long as you want
4. RDS Read Replicas for reading scalability
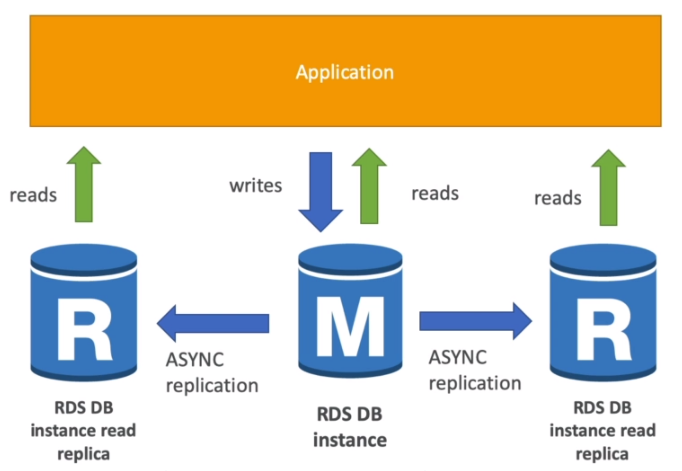
- Up to 5 Read Replicas
- Within AZ, Cross AZ or Cross-Region
- Replication is Async, so reads are eventually consistent
- Replicas can be promoted to their own DB
- Applications must update the connection string to leverage read replicas
4.1 Example

- You have a production database that is taking on normal load
- You want to run a reporting application to run some analytics
- You create a Read Replica to run the new workload there
- The production application is unaffected
- Read replicas are used for SELECT(=read) the only kind of statements(not INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
5. Security
5.1 At rest encryption
- Possibility to encrypt the master & read replicas with AWS Key Management System(KMS)-Advanced Encryption Standard(AES)-256 encryption
- Encryption has to be defined at launch time
- If the master is not encrypted, the read replicas cannot be encrypted
- Transparent Data Encryption(TDE) available for Oracle and SQL Server
- Is done only when you first create the DB instance, or unencrypted DB => snapshot => copy snapshot as encrypted => create DB from snapshot
5.2 In-flight encryption
- SSL certificates to encrypt data to RDS in flight
- Provide SSL options with trust certificate when connecting to database
- To enforce SSL:
- PostgreSQL: red.force_ssl= 1 in the AWS RDS Console(Parameter Groups)
- MySQL: Within the DB:
- GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'mysqluser'@'%' REQUIRE SSL;
5.3 RDS Encryption Operations
5.3.1 Encypring RDS backups
- Snapshots of un-encrypted RDS databases are un-encrypted
- Snapshots of encrypted RDS databases are encrypted
- Can copy a snapshot into an encrypted one
5.3.2 To encrypt an un-encrypted RDS database:
- Create a snapshot of the un-encrypted database
- Copy the snapshot and enable encryption for the snapshot
- Restore the database from the encrypted snapshot
- Migrate applications to the new database, and delete the old database
5.4 Network and IAM
5.4.1 Network Security
- RDS databases are usually deployed within a private subnet, not in a public one
- RDS security works by leveraging security groups(the same concept as for EC2 instances) - it controls which IP/security group can communicate with RDS
5.4.2 Access Management
- IAM policies help control who can manage AWS RDS (through the RDS API)
- Traditional Username and Password can be used to login into the database
- IAM-based authentication can be used to login into RDS MySQL & PostgreSQL
5.4.3 IAM Authentication
- IAM database authentication works with MySQL and PostgreSQL
- You don't need a password, just an authentication token obtained through IAM & RDS API calls
- Auth token has a lifetime of 15 minutes

- Network in/out must be encrypted using SSL
- IAM to centrally manage users instead of DB
- Can leverage IAM Roles and EC2 Instance profiles for easy integration
6. RDS vs EC2: Which one to choose?
6.1 RDS
- It allows you to outsource tasks like provisioning of the database, updating versions, and security to Amazon
- RDS allows you to focus on important tasks like performance tuning and schema optimization of your database
- You wouldn't have to manually set up database mirroring and failover clusters because you get highly optimized database solutions and synchronous Multi-AZ replication
- At times of disasters, you don't have to worry about managing your backups as RDS automates this process
6.2 MySQL on EC2
- It gives you full control over your database, OS, and software stack
- EC2 allows you to hire your own database administrators. They will help you manage your database by looking after backups, replication, and clustering
- You can use SQL Server features that are not currently supported by Amazon RDS
- It allows you to exceed your maximum database size and performance needs
- With EC2, you can set up a disaster recovery solution in SQL Server with AWS as the source
6.3 Performance
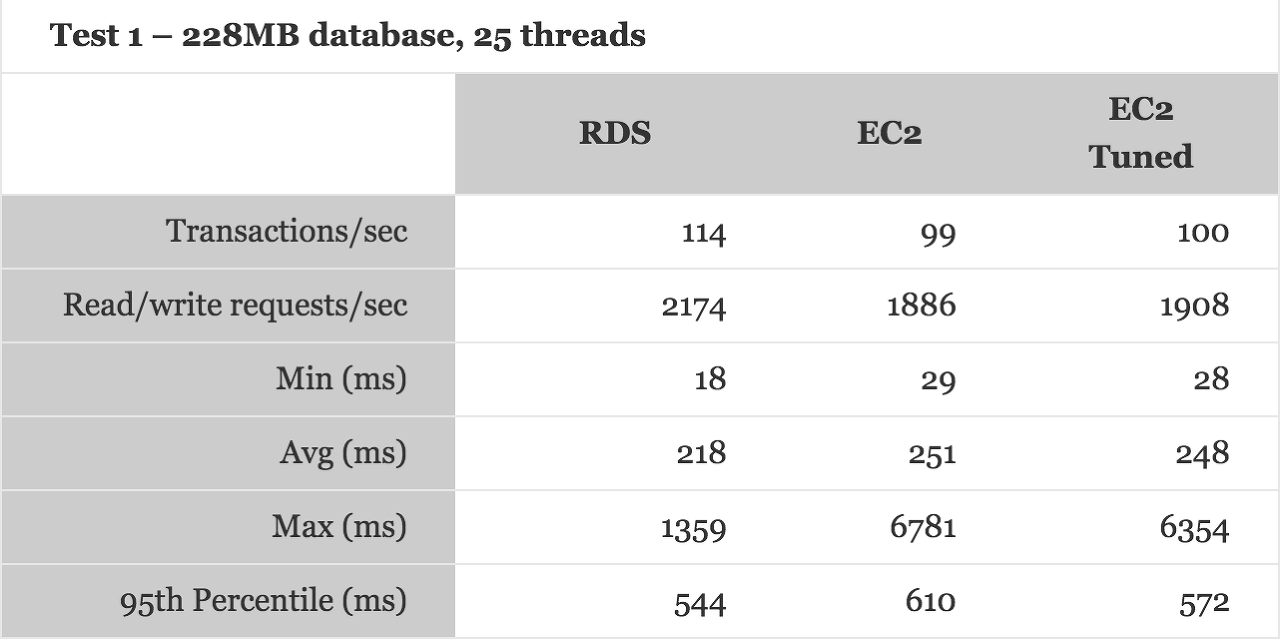
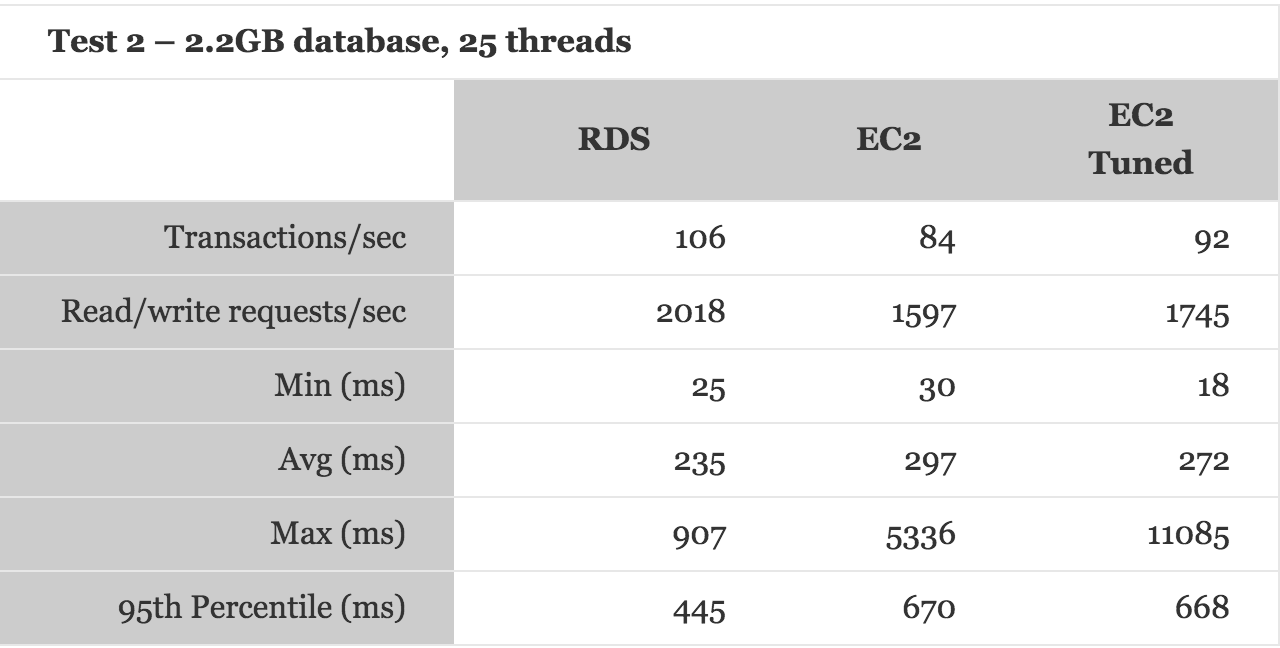
6.4 Costs
6.3.1 MySQL on EC2
- Instances: 3 x m2.4xlarge
- Storage: 3 1Tb EBS volumes (provisioned IOPS - 3000 IOPS) + 100Gb/month of snapshots space
- Intra-Region Data Transfer: 40Gb/Month
- On-demand instances: USD $3440 per month
- Reserved instances (1 year, partial upfront): USD $1466 per month
6.3.2 MySQL RDS
- Instance type: 1 x db.r3.2xlarge + 1 x db.r3.2xlarge (read replica)
- Multi-AZ: Yes
- Storage: 1Tb (provisioned IOPS - 3072 IOPS, one for each instance)
- Backup space: 100Gb/month
- Instra-Region Data Transfer: 40Gb/Month
- On-demand instances: USD $2484 per month
- Reserved instances (1 year, partial upfront): USD $1387 per month
7. Reference
serverguy.com/comparison/pros-cons-rds-vs-ec2-mysql-aws/
serverfault.com/questions/601548/cant-find-the-private-ip-address-for-my-amazon-rds-instance
'Cloud > AWS' 카테고리의 다른 글
CloudFront (0) 2020.11.24 ElasticBeanStalk (0) 2020.08.02 Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) (0) 2020.07.12 Serverless Architecture in AWS and Serverless Application Model(SAM) (0) 2020.07.11 Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) (0) 2020.07.10