-
ReentrantReadWriteLockStaticPL/JAVA 2020. 2. 27. 11:48
1. Overview
2. ReentrantReadWriteLock
2.1 Why
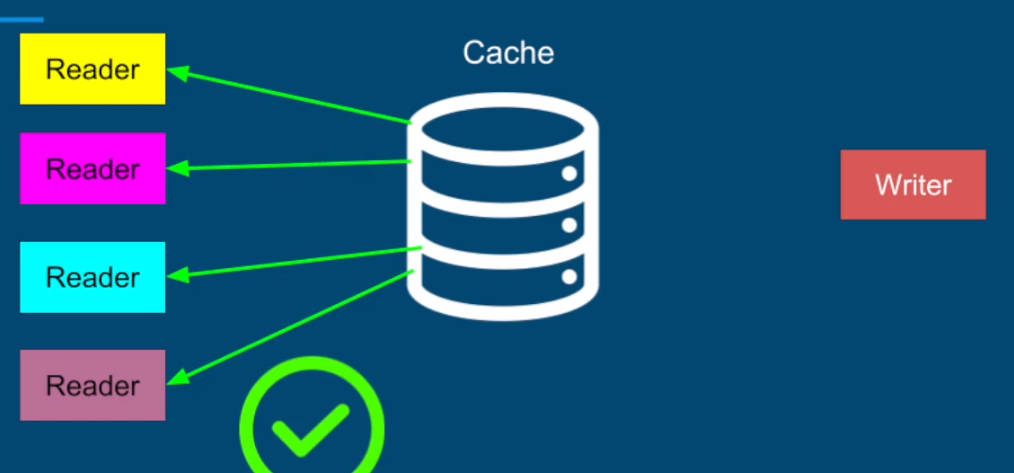
Multiple threads can safely read from a shared resource concurrently as long as they are not modifying its state.
2.2 Usage
- Synchronized and ReentrantLock do not allow multiple readers to access a shared resource concurrently.
- Not a big problem in the general case
- If we keep the critical sections short, the chances of contention over a lock are minimal
2.3 When to use
- When read operations are predominant
- Or when the read operations are not as fast
- Read from many variables
- Read from a complex data structure
- Mutual exclusion of reading threads negatively impacts the performance
2.4 How to use
ReentrantReadWriteLock rwLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); Lock readLock = rwLock.readLock(); Lock writeLock = rwLock.writeLock(); writeLock.lock(); try { modifySharedResource(); } finally { writeLock.unlock(); } readLock.lock(); try { readFromSharedResource(); } finally{ readLock.unlock(); }2.4 Mutual exclusion between readers and writers

3. Example

public class rerwlDemo { public static final int HIGHEST_PRICE = 1000; public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { InventoryDatabase inventoryDatabase = new InventoryDatabase(); Random random = new Random(); for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { inventoryDatabase.addItem(random.nextInt(HIGHEST_PRICE)); } Thread writer = new Thread(() -> { while (true) { inventoryDatabase.addItem(random.nextInt(HIGHEST_PRICE)); inventoryDatabase.removeItem(random.nextInt(HIGHEST_PRICE)); try { Thread.sleep(10); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }); writer.setDaemon(true); writer.start(); int numberOfReaderThreads = 7; List<Thread> readers = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < numberOfReaderThreads; i++) { Thread reader = new Thread(() -> { for (int j = 0; j < 100000; j++) { int upperBoundPrice = random.nextInt(HIGHEST_PRICE); int lowerBoundPrice = upperBoundPrice > 0 ? random.nextInt(upperBoundPrice) : 0; inventoryDatabase.getNumberOfItemsInPriceRange(lowerBoundPrice, upperBoundPrice); } }); reader.setDaemon(true); readers.add(reader); } long startReadingTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (Thread reader: readers) { reader.start(); } for (Thread reader: readers) { reader.join(); } long endReadingTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(String.format("Reading took %d ms", endReadingTime - startReadingTime)); } public static class InventoryDatabase { // the tree map which is implemented by a type of // binary search tree called red-black tree private TreeMap<Integer, Integer> priceToCountMap = new TreeMap<>(); private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); private ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantReadWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); private Lock readLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.readLock(); private Lock writeLock = reentrantReadWriteLock.writeLock(); public int getNumberOfItemsInPriceRange(int lowerBound, int upperBound) { // lock.lock(); readLock.lock(); try { Integer fromKey = priceToCountMap.ceilingKey(lowerBound); Integer toKey = priceToCountMap.floorKey(upperBound); if(fromKey == null || toKey == null) { return 0; } NavigableMap<Integer, Integer> rangeOfPrices = priceToCountMap.subMap(fromKey, true, toKey, true); int sum = 0; for (int numberOfItemsForPrice: rangeOfPrices.values()) { sum += numberOfItemsForPrice; } return sum; } finally { // lock.unlock(); readLock.unlock(); } } public void addItem(int price) { // lock.lock(); writeLock.lock(); try { Integer numberOfItemsForPrice = priceToCountMap.get(price); if (numberOfItemsForPrice == null) { priceToCountMap.put(price, 1); } else { priceToCountMap.put(price, numberOfItemsForPrice + 1); } } finally { // lock.unlock(); writeLock.unlock(); } } public void removeItem(int price) { // lock.lock(); writeLock.lock(); try { Integer numberOfItemsForPrice = priceToCountMap.get(price); if (numberOfItemsForPrice == null || numberOfItemsForPrice == 1) { priceToCountMap.remove(price); } else { priceToCountMap.put(price, numberOfItemsForPrice - 1); } } finally { // lock.unlock(); writeLock.unlock(); } } } }4. Reference
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/treemap-ceilingkey-in-java-with-examples/
'StaticPL > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
Non-blocking, Lock-free operations (0) 2020.02.27 Semaphore (0) 2020.02.27 ReentrantLock, lockInterruptibly, and tryLock (0) 2020.02.27 synchronized (0) 2020.02.27 Atomic Variables (0) 2020.02.26